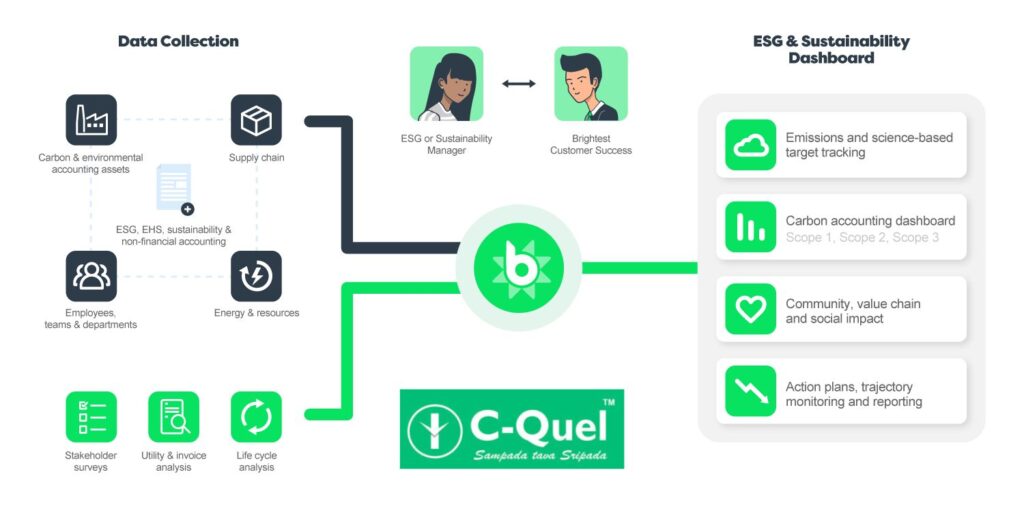
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) considerations have gained significant importance in the corporate world as businesses recognize the need to integrate sustainability and responsible practices into their operations. In India, the implementation of ESG principles has become a key focus for companies across various sectors. This blog post explores how ESG is being implemented in India, covering ESG solutions, ESG compliance, and the role of factory compliance in driving sustainable practices.
ESG Solutions in India
In recent years, a range of ESG solutions has emerged in India to help organizations assess and improve their environmental, social, and governance performance. These solutions encompass tools and frameworks for measuring, managing, and reporting on ESG metrics. Companies can leverage ESG rating agencies, such as Crisil, CARE Ratings, and ICRA, to evaluate their performance against ESG criteria and benchmark themselves against industry peers. Additionally, consultancy firms and sustainability experts offer tailored ESG solutions in India, helping businesses develop ESG strategies, set targets, and implement sustainable practices.
ESG Compliance in India
ESG compliance in India involves adhering to regulatory requirements and voluntary frameworks that promote sustainable and responsible business practices. The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has introduced guidelines for ESG disclosure and reporting, making it mandatory for listed companies to disclose their ESG initiatives in their annual reports. Moreover, the Companies Act, 2013, requires certain companies to allocate a percentage of their profits towards corporate social responsibility (CSR) activities, further emphasizing the integration of social and environmental considerations into business operations.
Factory Compliance in India
Factory compliance plays a crucial role in implementing ESG practices in India, particularly in the context of environmental sustainability and social responsibility. Environmental compliance ensures that factories adhere to pollution control norms, waste management regulations, and energy conservation measures. Social compliance focuses on labor rights, occupational health and safety, and fair employment practices. Various initiatives, such as the National Green Tribunal (NGT) and labor welfare boards, enforce factory compliance standards to drive sustainable operations and protect workers’ rights.
Conclusion:
ESG implementation in India is gaining momentum as businesses recognize the significance of sustainable practices and responsible corporate behavior. ESG solutions, ESG compliance, and factory compliance in India are integral components of this process, enabling organizations to assess, improve, and report on their ESG performance. By embracing ESG principles, companies in India can enhance their competitiveness, build trust with stakeholders, and contribute to the country’s sustainable development goals. Embracing ESG is not only a responsibility but also an opportunity for Indian businesses to create a positive impact on society and the environment.